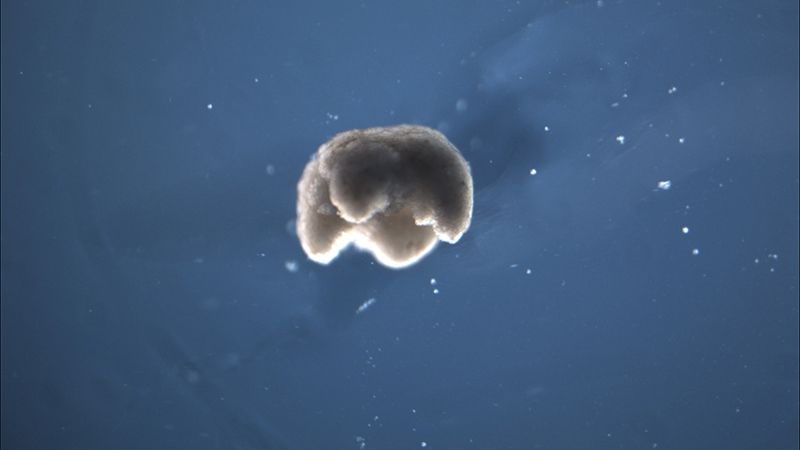
Scientists finally developed living programmable organisms using frog embryo cells. The recently developed self-mending animal are called ‘xenobots’ and can approach towards targets. They may likewise help in consisting medicine inside a patient’s body or lead comparable work.
These animals were planned on a supercomputer at UVM and afterward gathered and tried by scholars at Tufts University, who reaped foundational microorganisms from the incipient organisms of African frogs, the species Xenopus laevis.
Co-pioneer Michael Levin who coordinates the Center for Regenerative and Developmental Biology at Tufts says that they can look out mixes or radioactive tainting, can be utilized for social event microplastic in the seas, or for heading out in corridors to scratch out plaque.
The aftereffects of the new research were disclosed on January 13 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Individuals have been controlling creatures for human advantage since long and hereditary altering is getting broad with time, and a couple of counterfeit living beings have been physically amassed in the previous scarcely any years duplicating the body types of known creatures.
Numerous advancements are made of steel, concrete or plastic. That can make them solid or adaptable. Yet, they additionally can make environmental and human medical issues, similar to the developing scourge of plastic contamination in the seas and the poisonous quality of numerous engineered materials and gadgets.
A computer scientist and robotics expert from University of Vermont, Joshua Bongard said, “These are novel living machines. They’re neither a traditional robot nor a known species of animal. It’s a new class of artefact: a living, programmable organism.”
Norman Pearlstine is the Chief Editor of News Raise and focuses on Business news. His responsibility is to oversee the editorial content including business, commodities, personal investments and the stock market.